Picture this: three amateur fossil hunters in South Dakota stumble upon a skull that looks like it belongs in a fantasy novel rather than a paleontology textbook. With its spiky projections, horned appearance, and dragon-like features, this discovery would ignite one of the most fascinating debates in modern paleontology. The specimen they found would eventually bear one of the most memorable names in dinosaur history, connecting the worlds of science and popular culture in ways nobody expected.
The Discovery That Changed Everything
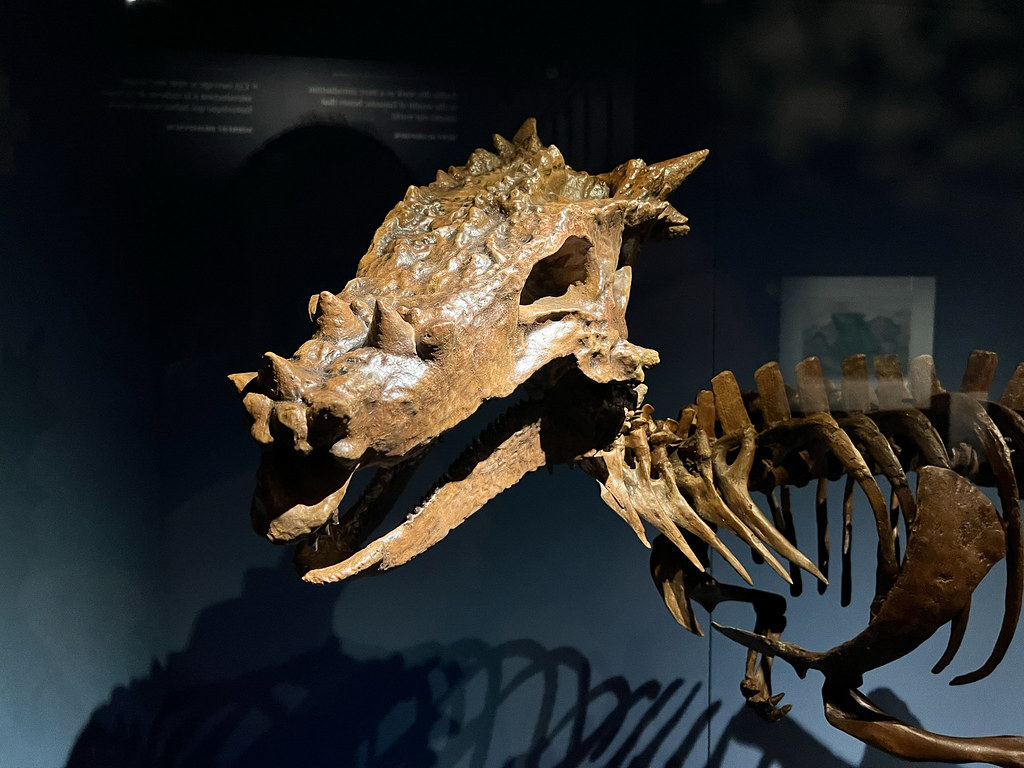

In 2004, the badlands of South Dakota yielded a treasure that would capture imaginations worldwide. Three fossil enthusiasts – Brian Buckmeier, Steve Saulsbury, and Patrick Saulsbury – unearthed what appeared to be a completely new species of dinosaur. The skull they discovered was unlike anything paleontologists had seen before, featuring dramatic spiky projections and an almost mythical appearance. What made this find particularly remarkable wasn’t just its unique features, but the pristine condition of the specimen. The skull was nearly complete, offering scientists an unprecedented view of what they believed was a previously unknown dinosaur species. The discovery site in the Hell Creek Formation, famous for its Late Cretaceous fossils, had once again proven to be a goldmine for paleontological research.
A Name Fit for Fantasy
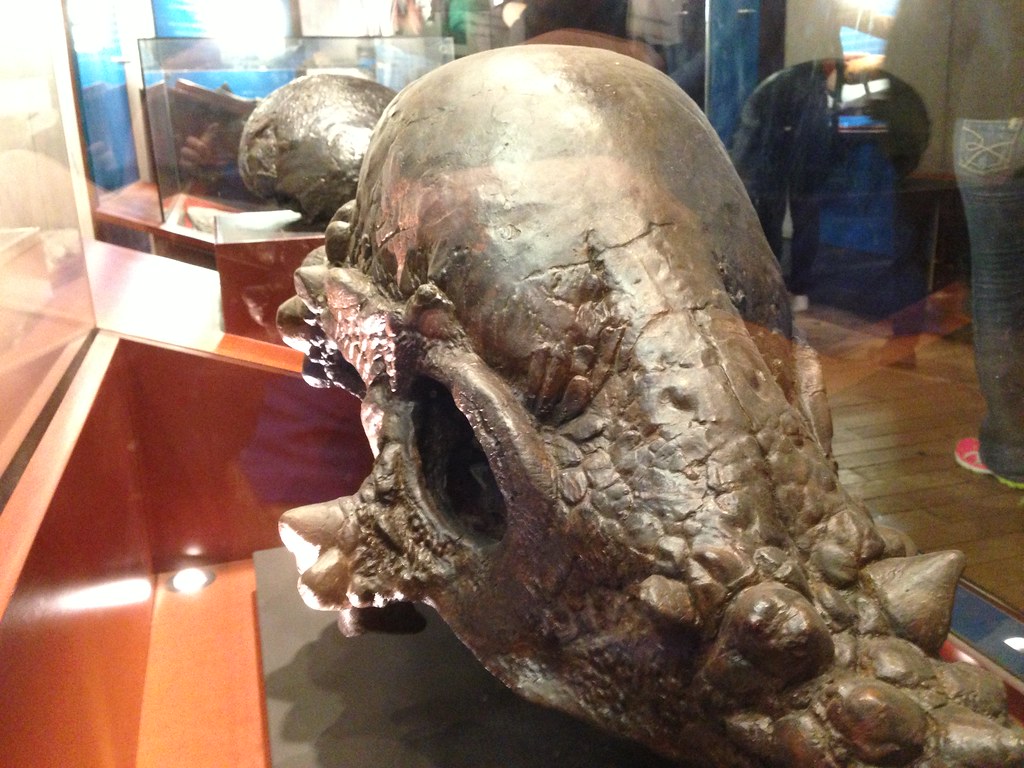

When it came time to officially name this dragon-like dinosaur, paleontologists Robert Bakker, Peter Larson, and Phil Currie made a decision that would make headlines around the world. They christened it Dracorex hogwartsia, combining the Latin words “draco” (dragon) and “rex” (king) with “hogwartsia” – a direct reference to Hogwarts School from the Harry Potter series. This wasn’t just a playful nod to popular culture; it was a strategic move to engage the public with paleontology. The name literally translates to “Dragon King of Hogwarts,” making it instantly memorable and accessible to people of all ages. The decision sparked conversations about how scientific naming conventions could evolve to better connect with contemporary culture while maintaining academic integrity. The naming ceremony itself became a media sensation, with the original discoverers donating the skull to the Children’s Museum of Indianapolis. This generous act ensured that future generations could marvel at this remarkable specimen while scientists continued their research.
Physical Features That Sparked Imagination
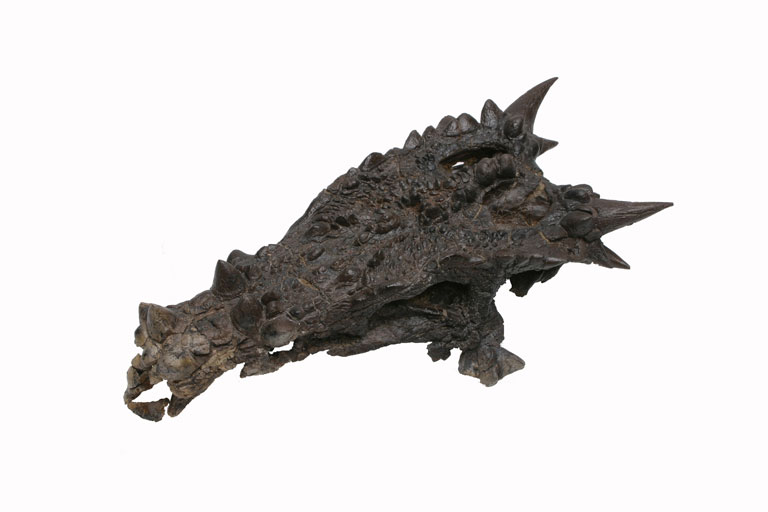

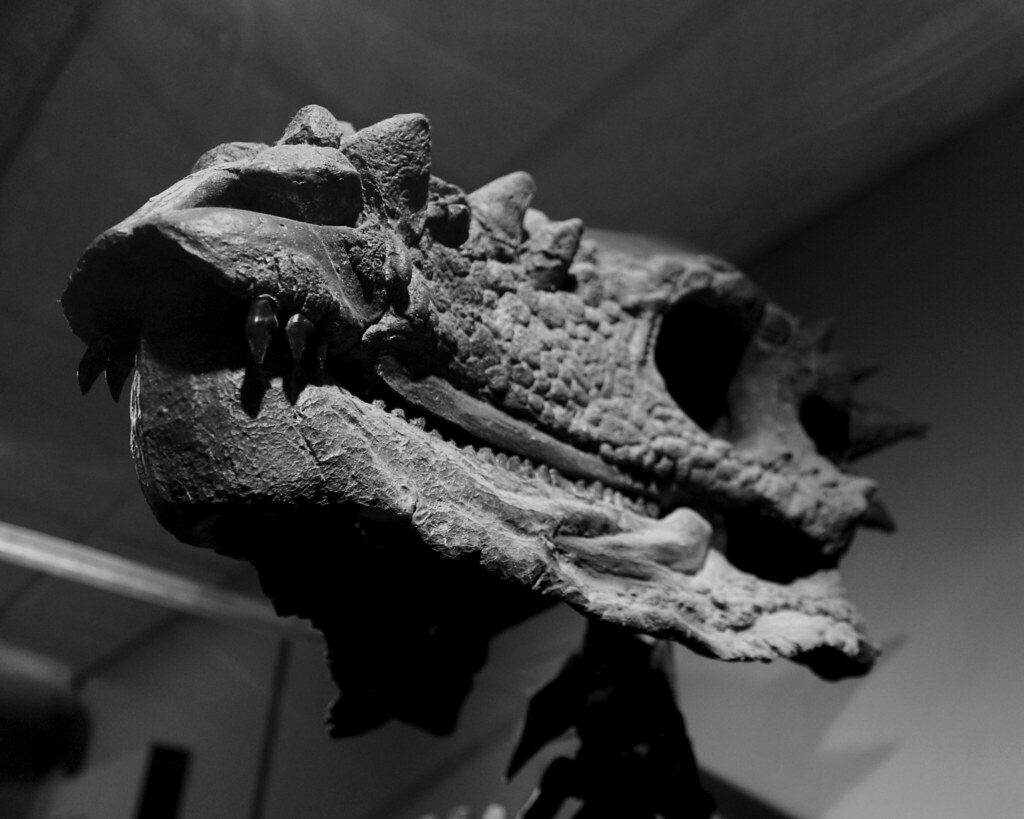
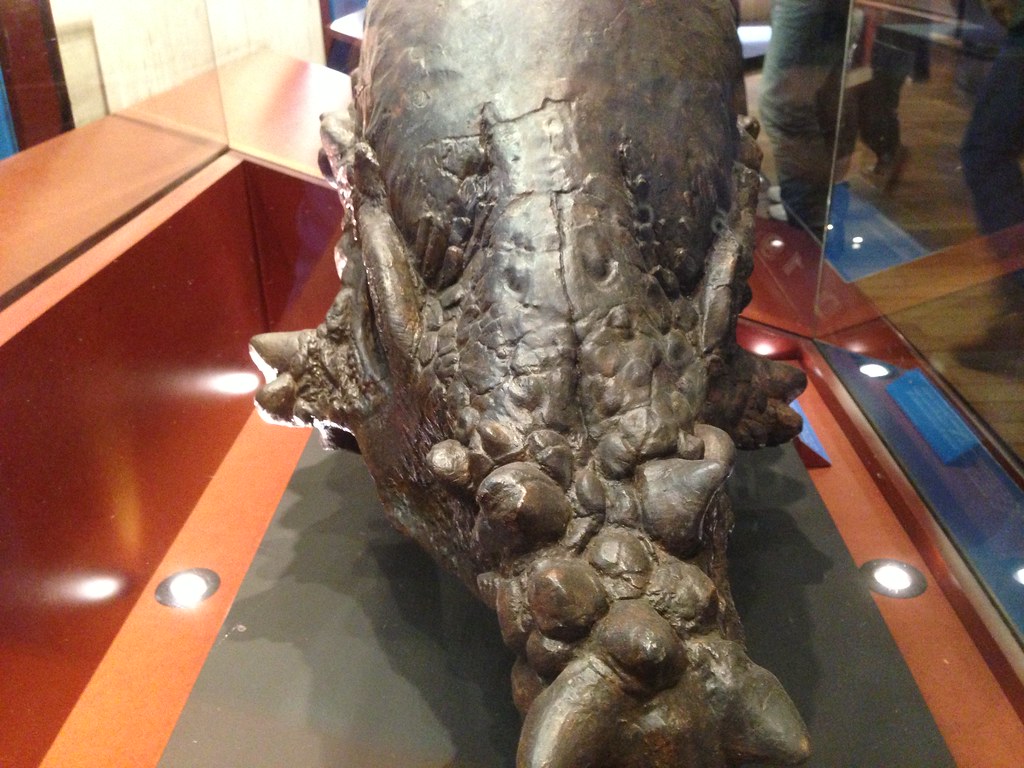
The Dracorex skull measured approximately two feet in length and displayed features that seemed almost too fantastical to be real. Multiple spiky projections adorned the top and back of the skull, creating a crown-like appearance that perfectly justified its dragon comparison. These weren’t just decorative features – they represented specialized bone structures that served specific biological purposes. The most striking aspect was the arrangement of these spikes, which varied in size and position across the skull. Some paleontologists noted similarities to modern horned lizards, suggesting these projections might have served defensive purposes or played roles in species recognition. The skull’s overall robust construction indicated this was no delicate creature, but rather a dinosaur built for survival in the challenging Late Cretaceous environment. What truly set Dracorex apart was the absence of the large frill typically associated with ceratopsian dinosaurs. Instead, the skull featured a more streamlined profile with its distinctive spiky ornamentation concentrated along the crown and posterior regions.
The Age Question That Started Everything
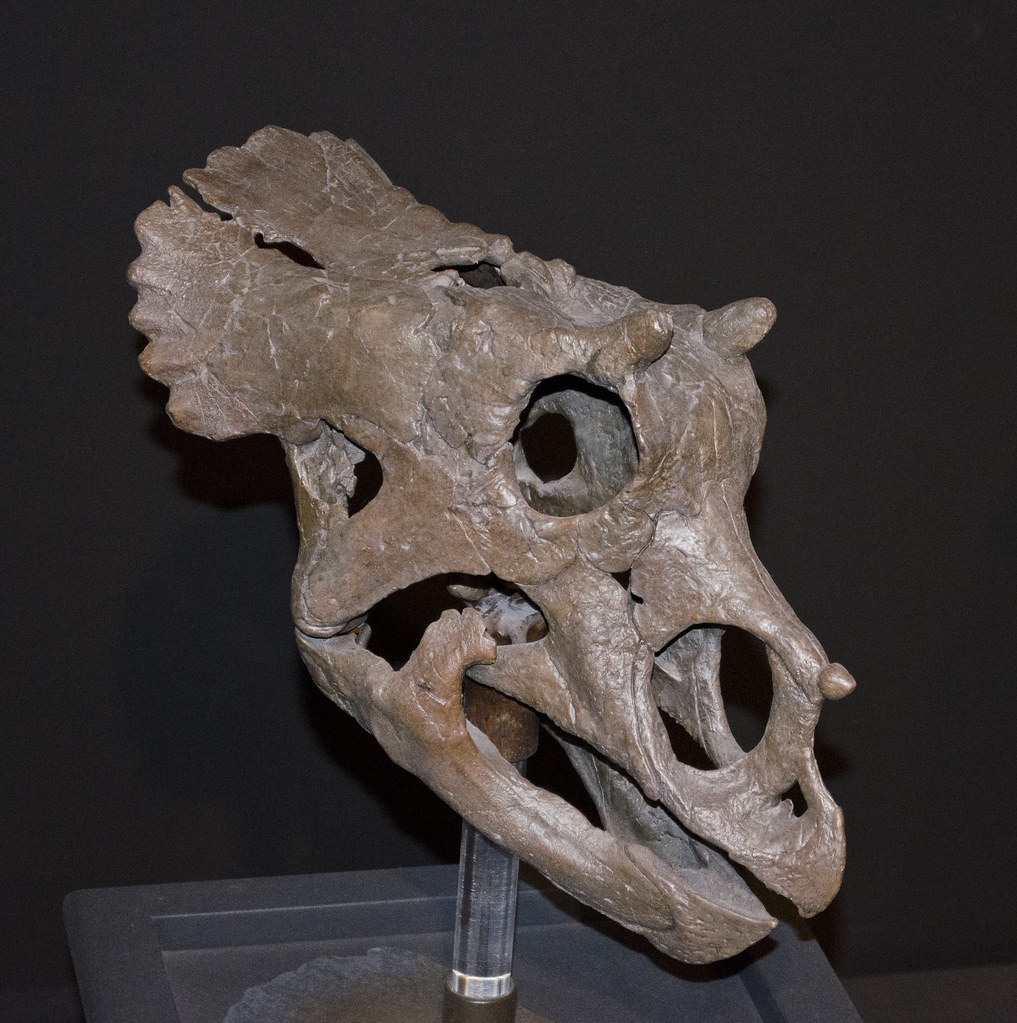

From the moment paleontologists began studying the Dracorex skull, questions arose about its age and development stage. The specimen appeared to represent a relatively young individual, based on various anatomical indicators including bone texture and suture patterns. This observation would prove crucial to the scientific debate that followed. Initial estimates suggested the Dracorex specimen died when it was still in its juvenile or sub-adult stage. The implications of this assessment were significant, as juvenile dinosaurs often looked dramatically different from their adult counterparts. Just as modern animals undergo substantial changes as they mature, dinosaurs experienced their own remarkable transformations during growth. The bone structure analysis revealed features consistent with active growth, suggesting this individual hadn’t reached its full adult size or development. This finding raised immediate questions about what an adult Dracorex might have looked like and whether the scientific community was dealing with a truly new species or something far more complex.
Enter the Pachycephalosaur Connection
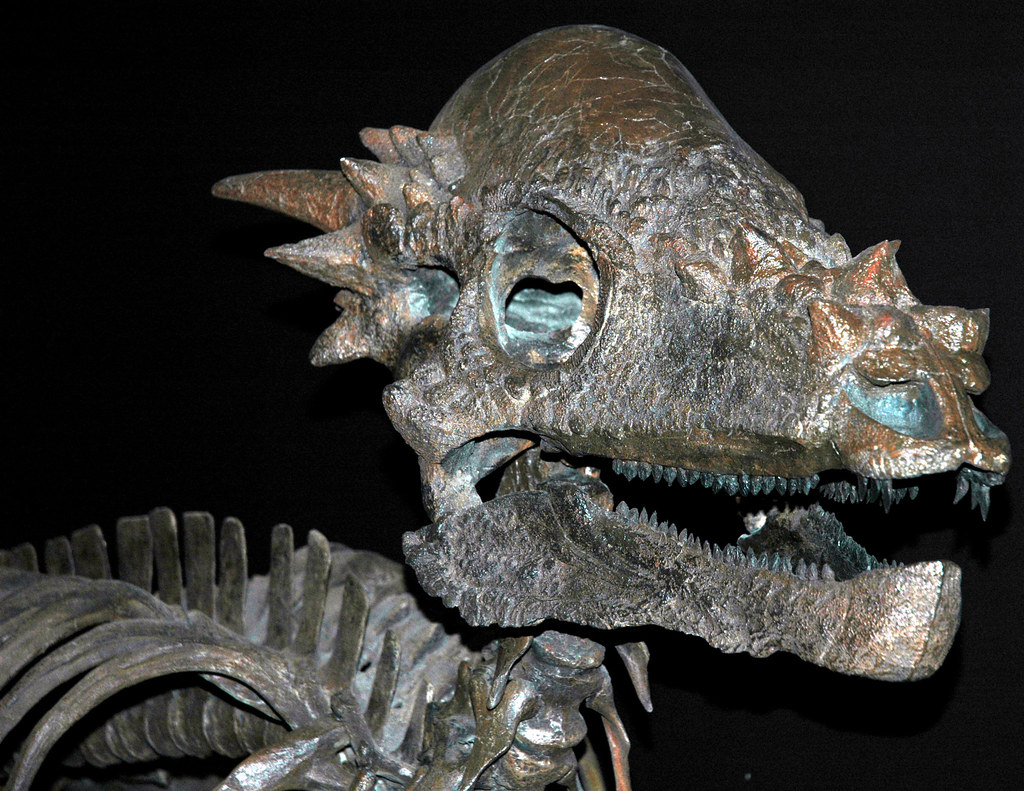

As research progressed, paleontologists began noticing striking similarities between Dracorex and known pachycephalosaur species. Pachycephalosaurs, the “thick-headed lizards,” were characterized by their dome-shaped skulls and were well-established members of the Late Cretaceous dinosaur community. The connection wasn’t immediately obvious, but careful analysis revealed telling similarities. The skull structure, despite its spiky appearance, shared fundamental architectural features with pachycephalosaur specimens. The braincase organization, the way certain bones connected, and even the overall proportions suggested a closer relationship than initially apparent. These observations led some researchers to propose that Dracorex might not be a separate species at all. What made this connection particularly intriguing was the geographic and temporal overlap between Dracorex and known pachycephalosaur species like Stygimoloch and Pachycephalosaurus. All three lived in the same region during the same time period, making the possibility of a developmental relationship much more plausible.
The Stygimoloch Mystery Deepens
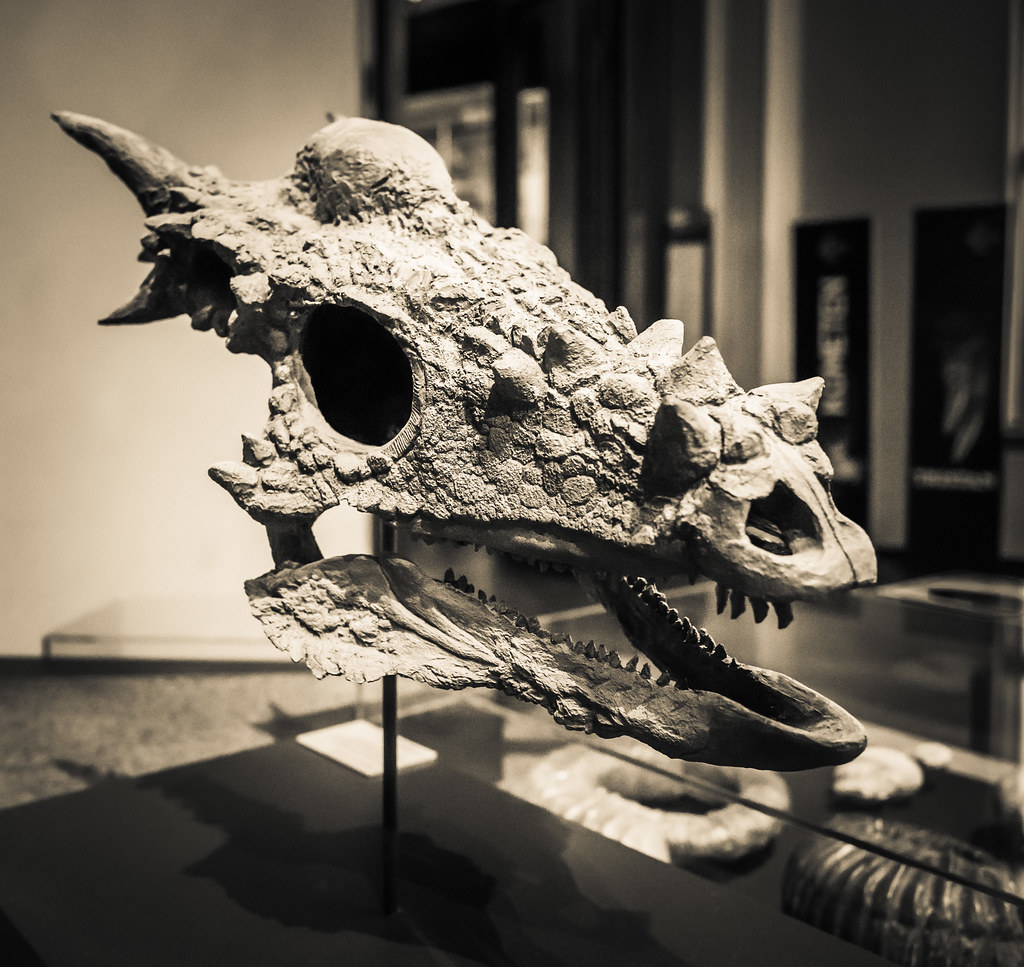

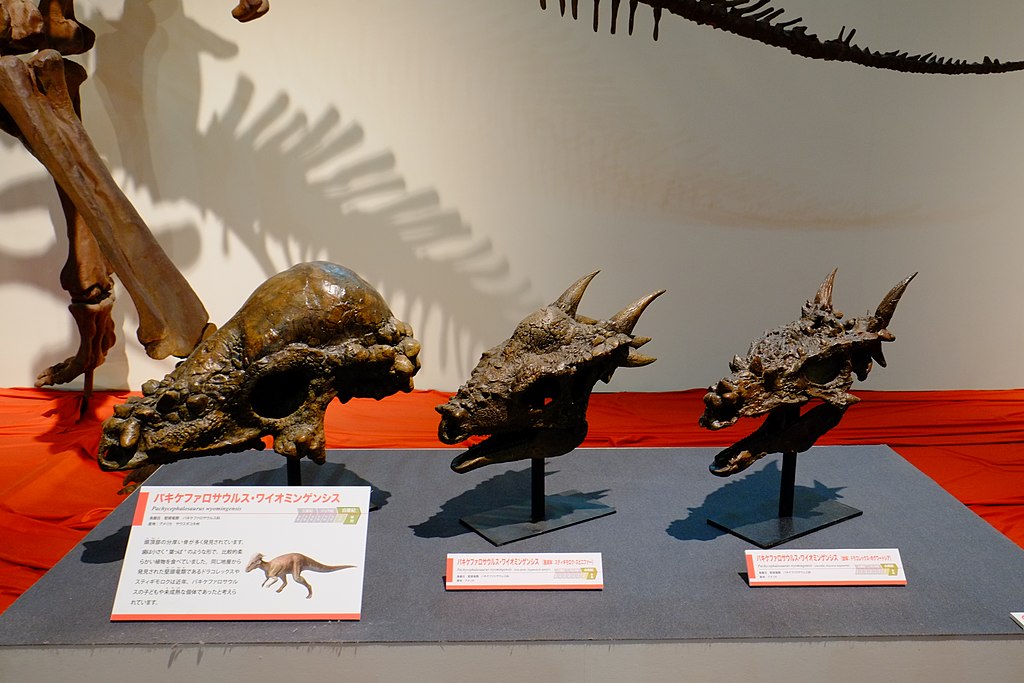
Stygimoloch spinifer, another spiky-skulled dinosaur from the same time and place as Dracorex, became a crucial piece of the puzzle. Originally described as its own species, Stygimoloch featured a skull adorned with long, pointed spikes that gave it an even more dramatic appearance than Dracorex. The similarities between these two species were impossible to ignore. When paleontologists compared the skulls side by side, they discovered what appeared to be a developmental progression. Dracorex skulls showed features that could logically develop into Stygimoloch characteristics with continued growth and maturation. The spike patterns, bone density, and overall architecture suggested a possible growth sequence rather than separate evolutionary lineages. This revelation transformed the scientific discussion from species identification to developmental biology. If Dracorex represented the juvenile form of what would eventually become Stygimoloch, then paleontologists were witnessing dinosaur development in unprecedented detail.
The Pachycephalosaurus Revelation
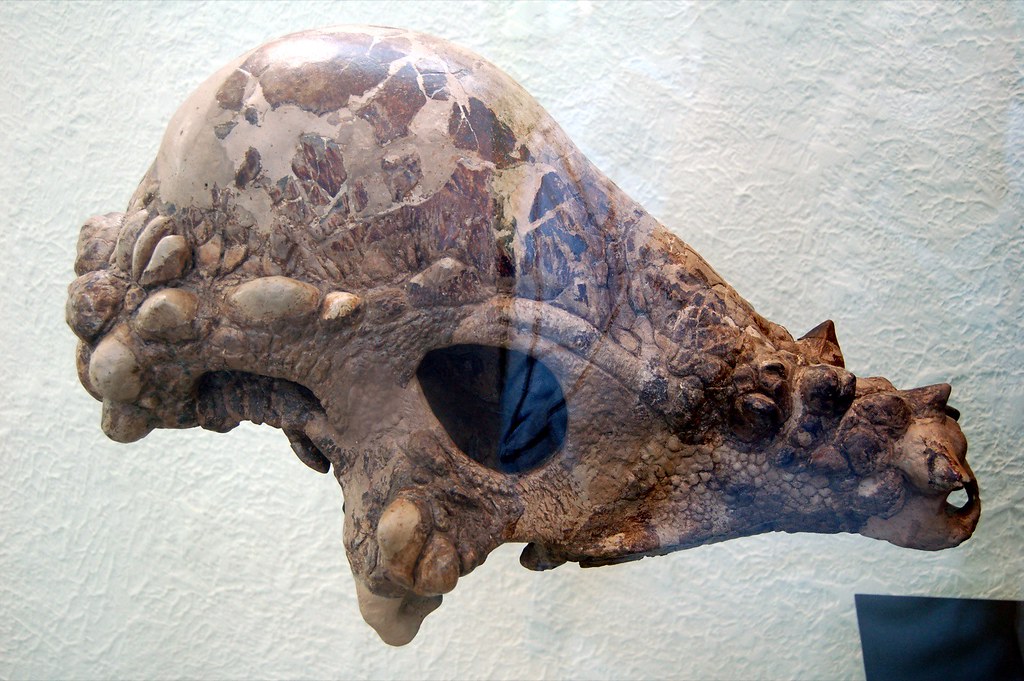
The plot thickened even further when researchers began examining the relationship between these spiky dinosaurs and Pachycephalosaurus wyomingensis, the classic dome-headed dinosaur. Pachycephalosaurus had been known to science for decades, with its characteristic thick, rounded skull dome making it one of the most recognizable dinosaur species. Could it be possible that Dracorex, Stygimoloch, and Pachycephalosaurus represented different growth stages of the same species? This revolutionary idea challenged everything paleontologists thought they knew about these dinosaurs. The evidence began mounting as researchers identified transitional features that could connect all three forms in a single developmental sequence. Computer modeling and detailed anatomical analysis revealed how the spiky projections of juvenile skulls could be reabsorbed and modified as the animal matured, eventually forming the characteristic dome of adult Pachycephalosaurus specimens. This process, known as ontogenetic change, is common in modern animals but had rarely been documented so clearly in dinosaur fossils.
Scientific Methods Behind the Investigation
The investigation into Dracorex’s true identity required cutting-edge scientific techniques and methodologies. Researchers employed computed tomography (CT) scanning to examine internal skull structures without damaging the precious fossils. These scans revealed details about bone density, growth patterns, and internal architecture that weren’t visible through traditional examination methods. Histological analysis, which involves studying thin sections of bone under microscopes, provided crucial insights into the age and growth stage of the specimens. The bone tissue patterns in Dracorex showed characteristics typical of rapidly growing juvenile animals, supporting the hypothesis that this wasn’t a fully mature individual. Comparative anatomy played a central role in building the case for developmental relationships. Scientists created detailed measurements and statistical analyses comparing skull features across all suspected growth stages. These quantitative approaches helped establish objective criteria for evaluating the developmental hypothesis beyond subjective visual similarities.
The Bone Histology Evidence
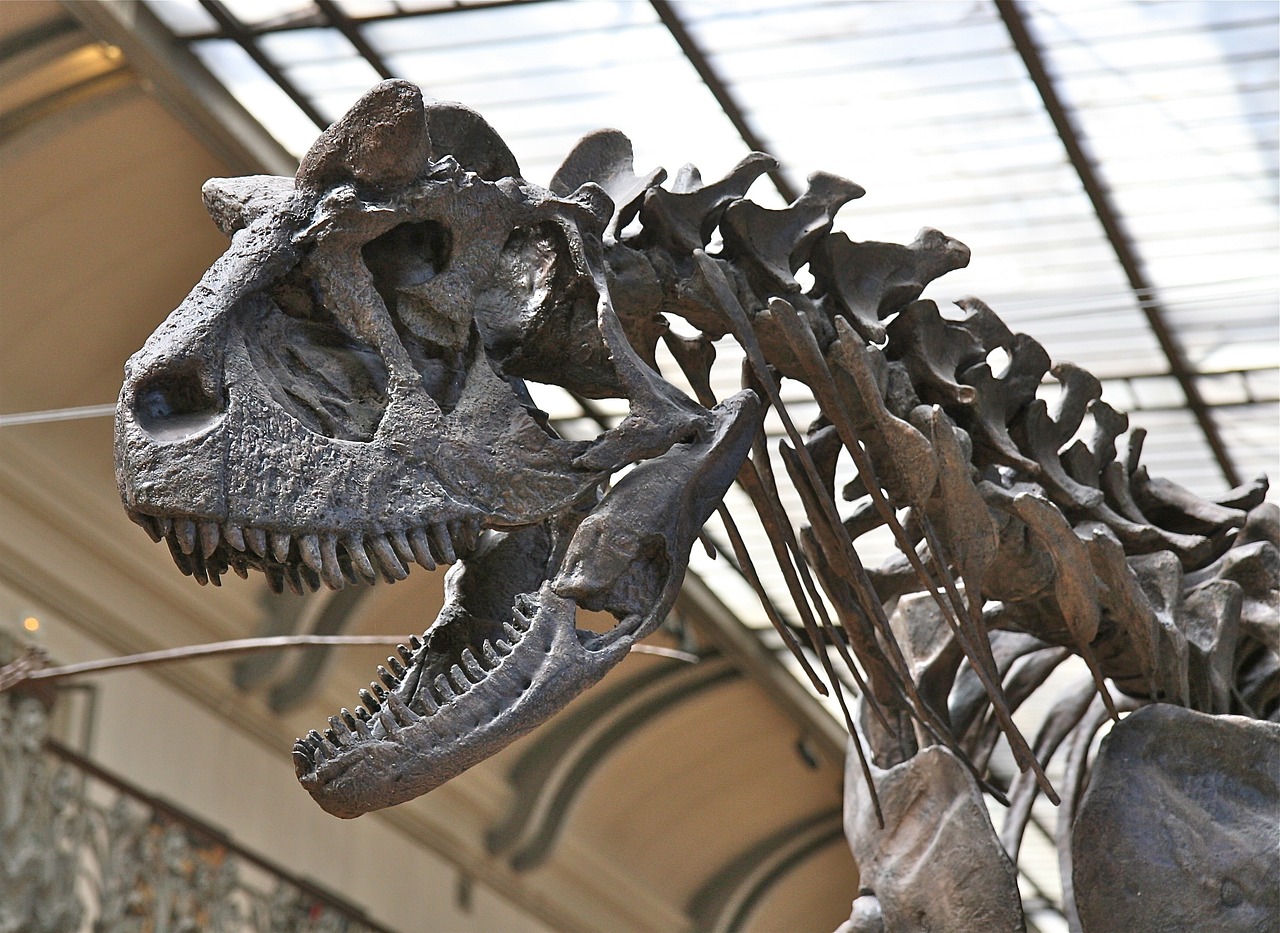

Perhaps the most compelling evidence for the developmental hypothesis came from microscopic examination of bone tissue. When paleontologists studied thin sections of bone from Dracorex, Stygimoloch, and Pachycephalosaurus specimens, they discovered clear patterns that supported a growth sequence interpretation. The bone tissue in Dracorex specimens showed features consistent with rapid juvenile growth, including well-vascularized bone structure and growth lines indicating active development. As specimens progressed through the proposed Stygimoloch stage, the bone tissue showed intermediate characteristics – still growing, but beginning to show signs of maturation. Adult Pachycephalosaurus specimens displayed mature bone tissue with slower growth rates and denser structure typical of fully developed individuals. This progression provided biological evidence that complemented the anatomical observations, creating a comprehensive picture of dinosaur development that had never been documented before.
Opposition and Alternative Theories

Not all paleontologists embraced the developmental hypothesis, and significant opposition emerged within the scientific community. Some researchers argued that the anatomical differences between the three forms were too substantial to represent simple growth stages of a single species. They pointed to specific features that seemed unlikely to change so dramatically during development. Critics also raised concerns about the statistical analysis methods used to support the developmental hypothesis. They argued that natural variation within species could account for many of the observed differences without requiring a complex growth sequence explanation. Some proposed that environmental factors or sexual dimorphism might explain the variations rather than age-related changes. Alternative theories suggested that these dinosaurs might represent closely related species that lived alongside each other, rather than different growth stages of the same animal. This interpretation would maintain the validity of all three species names while acknowledging their obvious relationships and similarities.
Implications for Dinosaur Diversity

The Dracorex debate has profound implications for how scientists understand dinosaur diversity and evolution. If the developmental hypothesis is correct, it means that paleontologists may have been overestimating the number of distinct dinosaur species by misidentifying different growth stages as separate species. This revelation could apply to other dinosaur groups as well, suggesting that juvenile and adult forms of many species might have been given different scientific names throughout paleontological history. The implications extend beyond simple taxonomy to affect our understanding of ancient ecosystems, population dynamics, and evolutionary relationships. The case also highlights the importance of finding complete growth series in fossil deposits. Without specimens representing all life stages, paleontologists might continue to misinterpret juvenile forms as distinct species, leading to inflated diversity estimates and incorrect evolutionary trees.
Modern Techniques Shed New Light
Advanced imaging and analysis techniques continue to provide new insights into the Dracorex controversy. High-resolution CT scanning allows researchers to examine internal skull structures with unprecedented detail, revealing features that were previously impossible to study without damaging valuable fossils. Three-dimensional modeling software enables scientists to visualize how skull features might change during growth, creating animations that show potential developmental transformations. These tools help bridge the gap between static fossil specimens and the dynamic processes that shaped them during life. Biomechanical analysis using computer simulations provides insights into how different skull configurations might have functioned in living animals. These studies help evaluate whether the proposed developmental changes make biological sense from an engineering and functional perspective.
Educational Impact and Public Engagement

The Dracorex story has become a powerful educational tool, demonstrating how scientific understanding evolves through careful research and debate. Museums worldwide use this case study to teach visitors about the scientific process, showing how new evidence can challenge established ideas and lead to better understanding. The Harry Potter connection continues to capture public imagination, drawing people into paleontology who might never have shown interest otherwise. This engagement has led to increased funding for fossil research and greater appreciation for the scientific method among general audiences. Educational programs built around the Dracorex story help students understand concepts like hypothesis testing, evidence evaluation, and the importance of keeping an open mind in scientific research. The controversy serves as a perfect example of how science progresses through questioning and investigation rather than accepting initial conclusions.
Current Scientific Consensus

Today, the majority of paleontologists accept the developmental hypothesis, viewing Dracorex as the juvenile form of what would eventually become Pachycephalosaurus. However, this consensus emerged gradually and continues to be refined as new evidence becomes available. The scientific process remains open to new discoveries that might modify or challenge current understanding. Recent studies have strengthened the case for developmental relationships by identifying additional specimens that fill gaps in the proposed growth sequence. These finds provide more data points along the continuum from spiky juvenile to dome-headed adult, making the transformation seem increasingly plausible. The acceptance of this hypothesis has led to changes in museum displays and educational materials worldwide. Dracorex is now typically presented as a juvenile Pachycephalosaurus rather than a distinct species, though its memorable name and dramatic appearance ensure it remains a public favorite.
Conclusion

The story of Dracorex hogwartsia represents more than just a case of mistaken identity in paleontology. It exemplifies how science progresses through careful observation, rigorous testing, and willingness to revise understanding when new evidence emerges. This dragon-named dinosaur may have lost its status as a unique species, but it gained something perhaps more valuable – a role as teacher and inspiration for future generations of scientists. The debate surrounding Dracorex has fundamentally changed how paleontologists approach new fossil discoveries, emphasizing the importance of considering developmental stages and growth patterns before declaring new species. It serves as a reminder that in science, the most exciting discoveries often come not from finding something entirely new, but from understanding familiar things in completely new ways. What started as a fantasy-inspired name for a dragon-like skull has evolved into a profound lesson about the complexity of life itself.




