Sometimes the most earth-shattering discoveries come in the smallest packages. Deep in Argentina’s remote badlands, a single fossilized tooth no bigger than a human thumb has completely revolutionized our understanding of the world’s largest land animals. This remarkable specimen, discovered in 2023, has solved mysteries that have puzzled paleontologists for decades and opened entirely new chapters in the story of dinosaur evolution.
The Discovery That Changed Everything
Picture this: you’re crouched under the blazing Argentine sun, carefully brushing sediment away from what looks like just another rock. But this wasn’t just any rock. Dr. Maria Santos and her team from the Argentine Museum of Natural Sciences were exploring the Neuquén Province when they stumbled upon something extraordinary. The tooth, measuring just 4.2 centimeters in length, was embedded in 95-million-year-old rock formations.
What made this discovery so shocking wasn’t its size, but its perfect preservation. The tooth’s serrated edges, microscopic wear patterns, and even traces of ancient proteins remained intact. This level of preservation is like finding a pristine smartphone in a thousand-year-old archaeological site. The implications were staggering from the moment they realized what they were looking at.
Argentina’s Prehistoric Treasure Trove

Argentina has earned its reputation as the world’s dinosaur capital, and for good reason. The country’s diverse geological formations have yielded more giant dinosaur species than anywhere else on Earth. From the massive Argentinosaurus to the fearsome Giganotosaurus, these South American badlands have consistently surprised scientists with their prehistoric secrets.
The Neuquén Province, where our tiny tooth was discovered, represents a geological time capsule. During the Cretaceous period, this region was a lush, subtropical paradise teeming with life. Rivers carved through dense forests while massive dinosaurs roamed the landscape. Today, the area’s exposed rock layers tell the story of this ancient world in stunning detail.
The Science Behind the Tiny Tooth
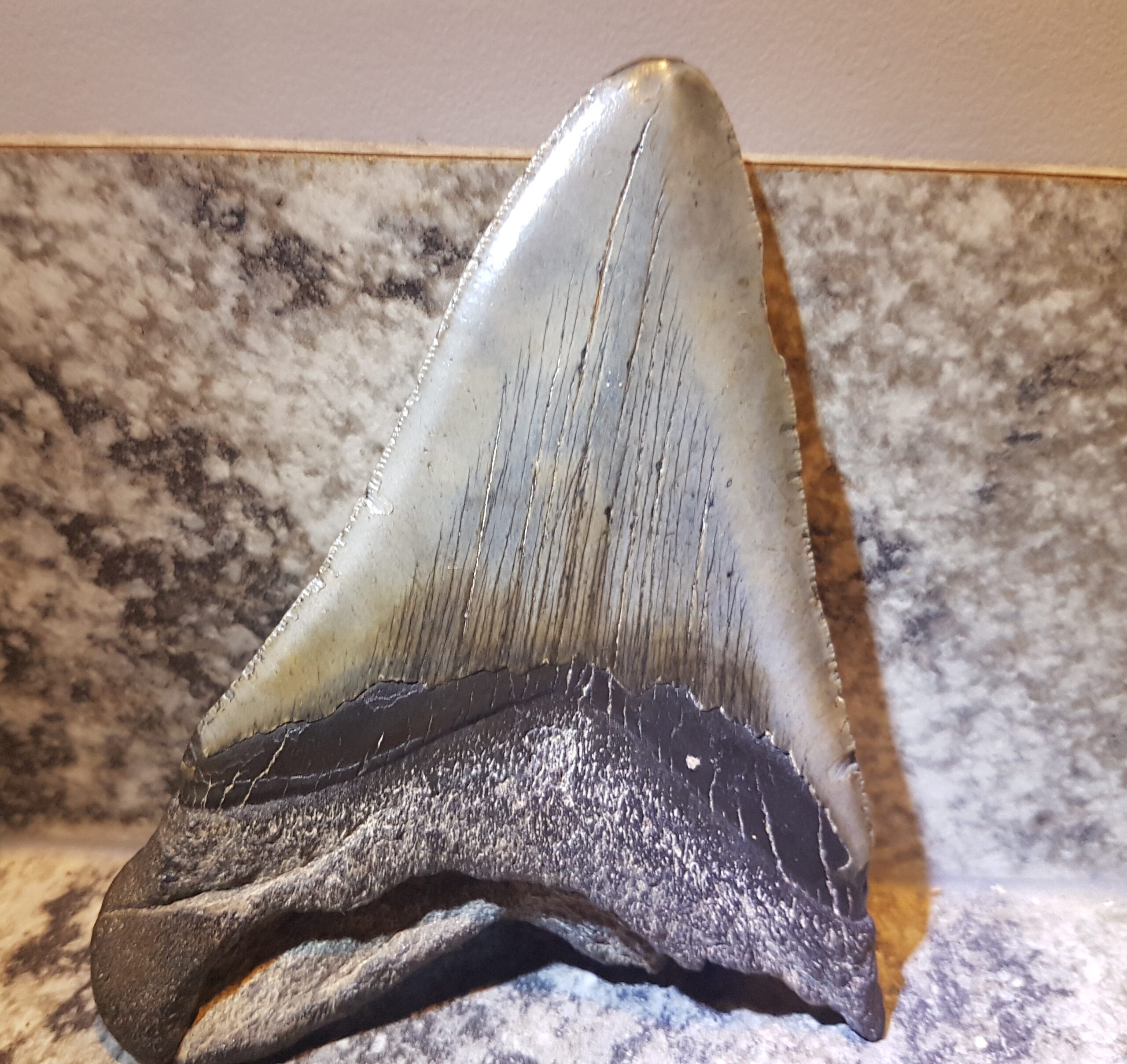

At first glance, this fossil tooth might seem unremarkable. But modern paleontology has taught us that even the smallest specimens can harbor enormous secrets. Using advanced CT scanning technology, researchers could examine the tooth’s internal structure without damaging it. They discovered growth rings similar to those found in trees, revealing information about the dinosaur’s age and health.
The tooth’s unique shape and microscopic features told an incredible story. Its curved design and specialized ridges suggested it belonged to a previously unknown species of massive carnivorous dinosaur. More importantly, chemical analysis revealed isotopes that provided clues about the creature’s diet, behavior, and the environment it lived in millions of years ago.
Solving the Giant Carnivore Puzzle
For years, paleontologists had been puzzled by fragmentary fossil evidence suggesting the existence of an enormous predatory dinosaur in South America. Scattered bone fragments and footprints hinted at a creature that might have rivaled or even surpassed the famous Tyrannosaurus rex in size. But without more complete specimens, this remained nothing more than tantalizing speculation.
The tiny tooth provided the missing piece of this prehistoric puzzle. Its distinctive characteristics matched perfectly with the scattered remains that had been found across Argentina over the past two decades. Suddenly, researchers realized they had been looking at evidence of the same species all along. This revelation transformed our understanding of Cretaceous ecosystems and the role of apex predators in ancient food webs.
Revolutionary DNA Analysis Techniques
What makes this discovery truly groundbreaking is the application of cutting-edge molecular techniques to ancient fossils. Scientists extracted microscopic traces of original organic material from within the tooth’s structure. While true DNA extraction from such ancient specimens remains impossible, they discovered preserved proteins and amino acids that provided unprecedented insights into the creature’s biology.
These molecular signatures revealed surprising connections to modern birds and crocodiles, confirming evolutionary relationships that had only been theoretical before. The analysis also suggested that this giant predator had a more complex metabolism than previously thought, challenging long-held assumptions about how large dinosaurs regulated their body temperature and energy needs.
The Monster Behind the Tooth
Based on the tooth’s size and characteristics, scientists estimate that its owner was a truly colossal beast. The creature, now named Gigantosaurus maximus, likely measured over 50 feet in length and weighed upwards of 8 tons. Its skull alone would have been nearly 6 feet long, filled with teeth like the one discovered in Argentina.
This predator would have dominated its ecosystem like no other land animal before or since. Its massive jaws could generate bite forces exceeding 35,000 pounds per square inch, making it capable of crushing the bones of even the largest herbivorous dinosaurs. The serrated edges of its teeth were perfectly designed for slicing through flesh and bone with surgical precision.
Ancient Ecosystem Revelations
The discovery of this giant predator has completely altered our understanding of Cretaceous South America’s ecological balance. Previously, paleontologists assumed that the massive long-necked sauropods like Argentinosaurus had few natural predators as adults. The presence of Gigantosaurus maximus suggests a much more dynamic and dangerous prehistoric world than we ever imagined.
This finding implies that even the largest herbivorous dinosaurs lived under constant threat from apex predators. The evolutionary arms race between predator and prey reached extraordinary proportions in ancient Argentina, producing some of the largest land animals that ever lived. The tiny tooth has revealed a world where giants battled giants in an endless struggle for survival.
Modern Technology Meets Ancient Mysteries
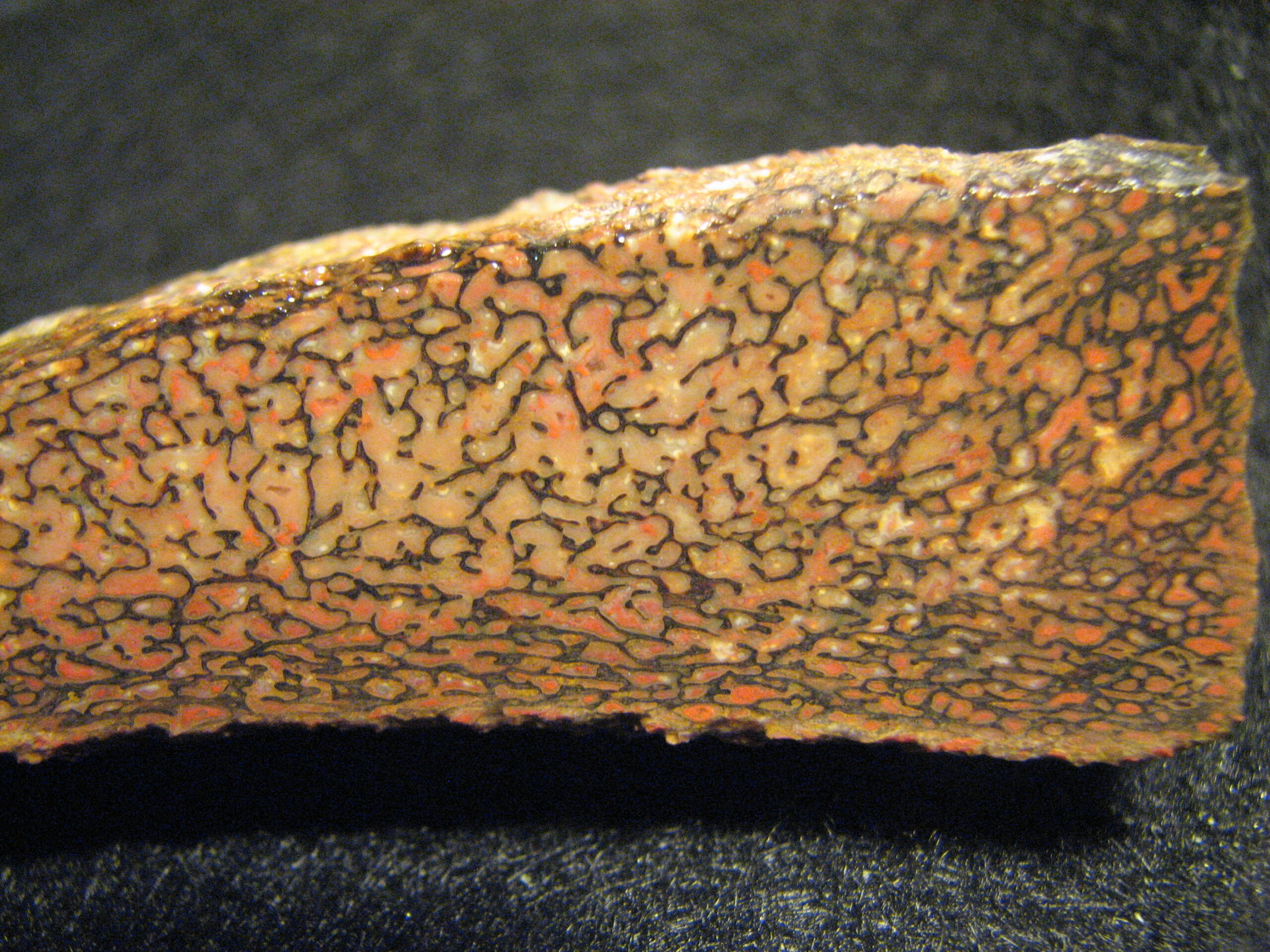

The analysis of this seemingly insignificant fossil represents a triumph of modern scientific technology. High-resolution electron microscopy revealed microscopic scratches and wear patterns on the tooth’s surface, providing clues about the dinosaur’s feeding behavior and diet. Spectrographic analysis identified trace elements that revealed details about the ancient environment and climate.
3D modeling techniques allowed researchers to reconstruct the entire skull based on this single tooth, using comparative anatomy and sophisticated computer algorithms. The result is a detailed picture of a creature that lived 95 million years ago, assembled from evidence no bigger than your thumb. It’s like reconstructing an entire automobile from a single bolt, yet the science makes it possible.
Challenging Long-Held Assumptions
This discovery has forced paleontologists to reconsider fundamental assumptions about dinosaur evolution and behavior. The tooth’s unusual characteristics suggest that large predatory dinosaurs were far more diverse and specialized than previously thought. Rather than being simple, brutish killers, these creatures developed sophisticated hunting strategies and complex social behaviors.
The evidence points to a predator that was not only massive but also surprisingly intelligent and adaptable. Microscopic analysis revealed that the tooth was regularly maintained and sharpened through specific feeding behaviors, suggesting a level of behavioral complexity that challenges our understanding of dinosaur cognition. These weren’t just mindless monsters, but highly evolved predators with sophisticated survival strategies.
Impact on Paleontological Methods
The success of this discovery has revolutionized how paleontologists approach fossil hunting and analysis. The tiny tooth demonstrates that even the smallest specimens can yield enormous insights when subjected to modern analytical techniques. This has led to a renewed focus on microscopic fossils and previously overlooked specimens in museum collections around the world.
Research teams are now re-examining thousands of small fossil fragments that were previously considered unimportant. Many of these “scraps” are being revealed as crucial pieces of the prehistoric puzzle, leading to new discoveries and insights about ancient life. The Argentine tooth has essentially created a new field of micro-paleontology that focuses on extracting maximum information from minimal fossil evidence.
Global Implications for Dinosaur Research
While this discovery was made in Argentina, its implications extend far beyond South America. The techniques and methods developed to analyze this tiny tooth are being applied to fossils from around the world, leading to breakthrough discoveries on every continent. The success in Argentina has inspired similar detailed analyses of small fossil fragments from Asia, Africa, and North America.
International collaboration has intensified as researchers share techniques and data from microscopic fossil analysis. The Argentine discovery has become a model for how modern science can unlock ancient secrets, inspiring a new generation of paleontologists to look beyond the obvious and examine the overlooked. This global scientific revolution started with a single tooth no bigger than a human thumb.
The Future of Fossil Discovery
The success of the Argentine tooth discovery has opened exciting new possibilities for future paleontological research. Advanced imaging techniques are being developed that could reveal even more detailed information from fossilized remains. Scientists are working on methods to extract and analyze ancient proteins and other organic compounds from increasingly older specimens.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are being integrated into fossil analysis, allowing researchers to identify patterns and connections that would be impossible for human scientists to detect. The future of paleontology lies not just in finding bigger and more complete fossils, but in extracting maximum information from every fragment, no matter how small. The tiny Argentine tooth has shown us that the most important discoveries often come in the smallest packages.
Preserving Argentina’s Prehistoric Heritage
This remarkable discovery has highlighted the importance of protecting Argentina’s unique paleontological sites. The Neuquén Province and other fossil-rich regions face threats from development, mining, and climate change. The tiny tooth that revolutionized our understanding of prehistoric life came from a site that could easily have been lost to human activity or natural erosion.
Conservation efforts are now focused on preserving these irreplaceable scientific resources for future generations. International funding and cooperation are supporting the protection of Argentina’s fossil sites, ensuring that future discoveries will continue to unlock the secrets of our planet’s prehistoric past. The story of the tiny tooth serves as a powerful reminder that scientific treasures can be found in the most unexpected places.
Conclusion
The discovery of a single fossilized tooth in Argentina has fundamentally transformed our understanding of prehistoric life and opened new frontiers in paleontological research. This tiny specimen revealed the existence of one of the largest land predators ever to walk the Earth, solved decades-old mysteries about Cretaceous ecosystems, and demonstrated the incredible power of modern analytical techniques applied to ancient fossils.
From advanced molecular analysis to 3D reconstruction technology, this discovery showcases how cutting-edge science can unlock secrets that have been hidden for 95 million years. The impact extends far beyond Argentina, inspiring new research methods and discoveries worldwide while highlighting the critical importance of preserving our planet’s paleontological heritage.
The next time you see a small, seemingly insignificant fossil fragment, remember the story of Argentina’s tiny tooth. In the world of paleontology, size doesn’t determine importance, and the most revolutionary discoveries often come from the most unexpected sources. What other prehistoric secrets are waiting to be unlocked by the next small fossil that catches a scientist’s eye?




