Imagine holding a key that could unlock thousands of years of forgotten history. Picture yourself standing before towering pyramids, their ancient stones whispering stories that no one has understood for over a millennium. For centuries, scholars stared at the mysterious hieroglyphs carved into Egyptian monuments, completely baffled by their meaning. These elegant symbols remained as cryptic as alien script until one remarkable discovery changed everything forever.
The Discovery That Changed History Forever

On a sweltering summer day in 1799, French soldier Pierre-François Bouchard was working on fortifications near the Egyptian town of Rosetta when his shovel struck something unusual. What he unearthed would become one of archaeology’s most significant treasures. The dark granite slab, measuring nearly four feet tall and two and a half feet wide, seemed ordinary at first glance.
But this wasn’t just any stone. Lieutenant Bouchard noticed three distinct sections of text carved into its surface, each written in a different script. The top section displayed the familiar hieroglyphs that had puzzled scholars for centuries. Below it, a middle section contained what appeared to be a different Egyptian script, and at the bottom, ancient Greek text stood clearly readable.
The discovery sent shockwaves through the scholarly world. Here was potentially the key that could finally unlock the mysteries of ancient Egyptian writing. Napoleon’s expedition had brought numerous scholars to Egypt, and they immediately recognized the stone’s incredible potential.
Three Scripts, One Message
The Rosetta Stone’s true genius lay in its trilingual nature. Ancient Egyptian priests had carved the same decree in three different scripts to ensure all segments of society could understand it. The hieroglyphic script at the top represented the sacred writing of the gods and royalty. The middle section, written in Demotic script, was the everyday writing system used by ordinary Egyptians.
The bottom section, inscribed in ancient Greek, proved to be the crucial breakthrough. Greek was a well-understood language among European scholars of the time. This meant they could read one-third of the stone’s message immediately, providing a potential roadmap to deciphering the Egyptian texts above.
The decree itself honored King Ptolemy V, celebrating his coronation and listing his achievements. While the content wasn’t particularly thrilling, the stone’s format created an unprecedented opportunity for linguistic comparison and analysis.
The Race to Crack the Code
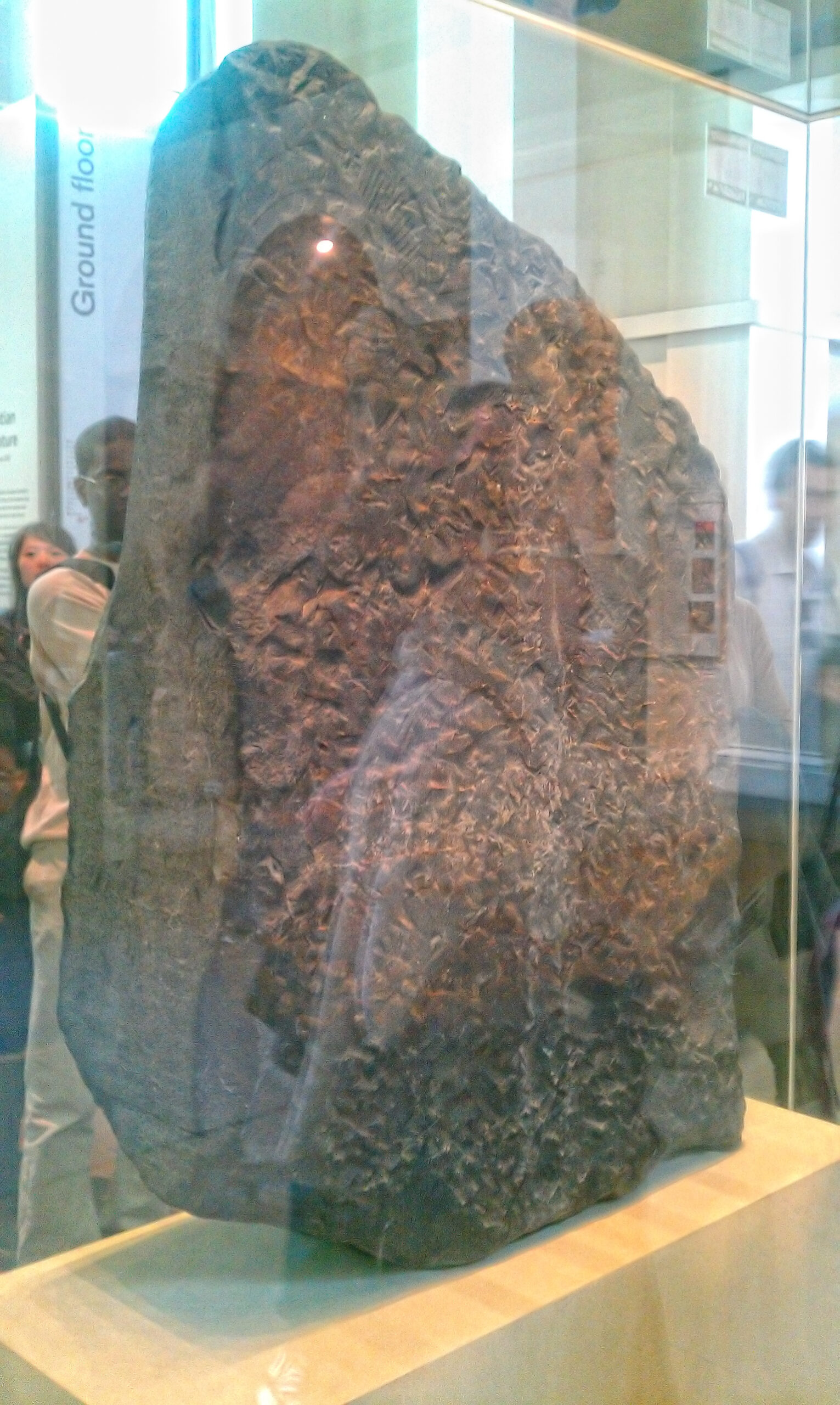

News of the Rosetta Stone’s discovery ignited a fierce competition among European scholars. Each wanted to be the first to unlock hieroglyphic writing and claim their place in history. The British seized the stone from the French in 1801, and it eventually found its way to the British Museum, where it remains today.
Thomas Young, a brilliant English physicist, made the first significant breakthrough. He correctly identified that the oval-shaped symbols called cartouches contained royal names. Young realized that hieroglyphs weren’t purely symbolic but could also represent sounds, just like letters in an alphabet.
However, Young’s progress stalled, and the torch passed to a young French scholar whose obsession with ancient languages would ultimately crack the code. The stage was set for one of history’s greatest intellectual achievements.
Jean-François Champollion: The Man Who Spoke to the Dead
Jean-François Champollion had been fascinated by ancient languages since childhood. By age sixteen, he was already fluent in Latin, Greek, Hebrew, Arabic, and Coptic. His passion for Egyptian hieroglyphs bordered on obsession, and he dedicated his entire adult life to understanding these mysterious symbols.
Champollion approached the problem differently than his predecessors. While others assumed hieroglyphs were purely symbolic, he suspected they combined both symbolic and phonetic elements. His knowledge of Coptic, the language of Christian Egypt, proved crucial because Coptic was the last surviving form of ancient Egyptian.
The breakthrough came in 1822 when Champollion was studying cartouches from other Egyptian monuments. He noticed repeated patterns and began matching them with known royal names. Suddenly, the symbols began revealing their secrets, and Champollion realized he was the first person in over a thousand years to truly read hieroglyphic writing.
The Moment of Breakthrough
The pivotal moment arrived when Champollion examined the name “Ramesses” written in hieroglyphs. He noticed that the same symbols appeared in multiple royal cartouches, suggesting they represented sounds rather than just concepts. The sun symbol, he realized, represented “Ra,” the Egyptian sun god, while other symbols spelled out the remaining sounds.
With trembling hands, Champollion began applying this phonetic principle to other hieroglyphs. Names like Cleopatra and Ptolemy suddenly became readable. The excitement was overwhelming as centuries of mystery began unraveling before his eyes.
Legend tells that Champollion burst into his brother’s office, shouted “I’ve got it!” and promptly fainted from the emotional intensity of his discovery. Whether true or not, this story captures the magnitude of his achievement perfectly.
Beyond Royal Names: Understanding the System

Champollion’s initial success with royal names was just the beginning. He discovered that hieroglyphic writing was far more complex than a simple alphabet. The system combined three different types of symbols: phonetic signs that represented sounds, ideographic signs that represented ideas or objects, and determinative signs that clarified meaning.
This complexity explained why previous scholars had struggled so much. Hieroglyphs weren’t just picture writing or alphabetic writing—they were a sophisticated combination of both. A single text might use a bird symbol to represent the sound “a,” the concept of “bird,” or serve as a determinative to clarify that the preceding word related to flying creatures.
Understanding this system required not just linguistic skill but also deep knowledge of Egyptian culture, religion, and daily life. Champollion spent years developing this comprehensive understanding, gradually building his ability to read increasingly complex texts.
The Floodgates Open: Reading Ancient Egypt
Once Champollion cracked the hieroglyphic code, the accumulated knowledge of ancient Egypt began pouring forth like water through a broken dam. Suddenly, temple walls, tomb inscriptions, and papyrus scrolls that had been silent for millennia began speaking again. The ancient Egyptians themselves became our guides to their world.
Religious texts revealed the complex mythology and beliefs that shaped Egyptian life. Administrative records showed how the kingdom was organized and governed. Personal letters provided intimate glimpses into the lives of ordinary people. Medical papyri demonstrated sophisticated knowledge of anatomy and healing practices.
The Rosetta Stone had unlocked not just a writing system but an entire civilization. Scholars could now read firsthand accounts of historical events, understand religious ceremonies, and even discover ancient Egyptian jokes and love poems.
Revolutionizing Our Understanding of Ancient Egypt
Before the Rosetta Stone’s decipherment, most knowledge about ancient Egypt came from Greek and Roman sources. These outsiders often misunderstood or misrepresented Egyptian culture. Now, for the first time, Egyptians could speak for themselves about their beliefs, achievements, and daily lives.
The hieroglyphic texts revealed a civilization far more sophisticated than previously imagined. Ancient Egyptians had developed complex philosophical ideas, advanced mathematical concepts, and detailed historical records. They weren’t the mysterious, primitive people that many had assumed.
Medical texts showed that Egyptian physicians performed surgery, set broken bones, and understood circulation centuries before similar knowledge appeared in Europe. Mathematical papyri revealed geometric principles used in pyramid construction and astronomical calculations for religious festivals.
The Technical Marvel of Translation

Champollion’s decipherment revealed the incredible sophistication of hieroglyphic writing. The system used over 700 different symbols, each with multiple potential meanings depending on context. Scribes had to master not just the symbols but also complex grammatical rules and cultural references.
Egyptian scribes wrote in various directions—left to right, right to left, or even vertically. They determined the reading direction by observing which way human and animal figures faced. This flexibility allowed for artistic arrangements that were both beautiful and functional.
The writing system also included punctuation marks, mathematical symbols, and even early forms of shorthand. Professional scribes held prestigious positions in Egyptian society, and their training took many years to complete.
Beyond the Rosetta Stone: Other Decipherment Tools
While the Rosetta Stone provided the initial breakthrough, Champollion and other scholars used additional sources to complete their understanding of hieroglyphic writing. Bilingual texts from temples, obelisks with Greek translations, and Coptic manuscripts all contributed crucial pieces to the puzzle.
The Philae Obelisk, discovered around the same time as the Rosetta Stone, contained another bilingual inscription that helped confirm Champollion’s theories. Multiple sources provided the redundancy needed to verify translations and build confidence in the decipherment method.
Modern scholars continue discovering new texts that refine our understanding of ancient Egyptian language. Each new find adds another piece to the enormous puzzle of Egyptian civilization.
The Cultural Impact of Understanding Hieroglyphs

The decipherment of hieroglyphs transformed how the world viewed ancient Egypt. No longer were Egyptians seen as mysterious builders of monuments to unknown gods. Instead, they emerged as real people with complex emotions, sophisticated knowledge, and relatable human experiences.
Egyptian literature revealed humor, wisdom, and beauty that resonated across millennia. Love poems showed that ancient Egyptians experienced the same romantic feelings as modern people. Wisdom texts contained advice about life, friendship, and success that remains relevant today.
The breakthrough also inspired broader interest in archaeology and ancient history. Museums worldwide began displaying Egyptian artifacts with new understanding, and the field of Egyptology was born as a serious academic discipline.
Modern Technology Meets Ancient Wisdom

Today’s scholars use advanced technology to study Egyptian texts in ways Champollion never imagined. Digital imaging reveals faded inscriptions invisible to the naked eye. Computer databases help scholars compare similar texts and identify patterns across thousands of documents.
Artificial intelligence assists in translating damaged or incomplete texts by suggesting likely missing words based on context and grammar patterns. These tools speed up translation work and help ensure accuracy in interpretation.
However, technology hasn’t replaced the need for human expertise. Understanding hieroglyphs still requires deep knowledge of Egyptian culture, history, and language. The combination of traditional scholarship and modern technology produces the most reliable translations.
Ongoing Discoveries and New Mysteries
Even today, new hieroglyphic texts continue to emerge from archaeological excavations across Egypt. Recent discoveries include administrative records from pyramid construction, personal letters from ancient workers, and religious texts that provide new insights into Egyptian beliefs.
Some texts still pose challenges for modern scholars. Highly specialized religious or scientific documents sometimes contain symbols or concepts that remain unclear. These mysteries remind us that ancient Egypt still holds secrets waiting to be unlocked.
The discovery of new texts also sometimes forces scholars to revise their understanding of Egyptian history and culture. Each new find has the potential to change our perception of this remarkable civilization.
The Rosetta Stone’s Legacy Today
The Rosetta Stone remains one of the most visited artifacts in the British Museum, drawing millions of visitors each year. Its simple appearance belies its tremendous historical significance. Most visitors stare at the carved symbols with wonder, perhaps imagining the excitement Champollion must have felt when he first understood their meaning.
The stone has also become a symbol for breakthrough discoveries and the power of human curiosity. The term “Rosetta Stone” is now used metaphorically to describe any key that unlocks previously hidden knowledge or understanding.
Modern language learning software even adopted the name “Rosetta Stone” to suggest that their programs provide a key to understanding foreign languages. This metaphorical use demonstrates how deeply the stone’s story has penetrated popular culture.
What We’ve Learned From Ancient Egyptian Voices
The decipherment of hieroglyphs has revealed ancient Egyptians as remarkably sophisticated people who grappled with many of the same questions that concern us today. They wondered about the meaning of life, worried about their children’s futures, and sought to understand their place in the universe.
Egyptian medical texts show that ancient physicians understood the importance of hygiene, performed complex surgeries, and developed treatments for various ailments. Their mathematical knowledge enabled them to build monuments that still amaze modern engineers.
Perhaps most importantly, we’ve learned that human nature hasn’t changed much over the millennia. Ancient Egyptians laughed at jokes, fell in love, mourned their dead, and celebrated life’s joys just as we do today. The Rosetta Stone didn’t just unlock a writing system—it opened a window into the timeless human experience.
The Continuing Journey of Discovery
The story of the Rosetta Stone reminds us that sometimes the greatest discoveries come from unexpected places. A French soldier’s routine excavation work led to one of archaeology’s most significant breakthroughs. This pattern continues today as archaeologists working in Egypt regularly uncover new texts and artifacts.
Modern excavations use sophisticated techniques that would astound Champollion. Ground-penetrating radar reveals hidden chambers before digging begins. Satellite imagery helps identify potential archaeological sites across vast areas of desert.
Yet the fundamental excitement remains the same. When archaeologists uncover a new text or artifact, they experience the same thrill of discovery that Champollion felt nearly two centuries ago. Each find has the potential to add new chapters to our understanding of ancient Egypt.
The Rosetta Stone transformed our understanding of ancient Egypt from mysterious speculation to factual knowledge. Champollion’s breakthrough opened thousands of years of recorded history, revealing a civilization of remarkable sophistication and humanity. The stone’s three scripts provided the key that unlocked not just a writing system but an entire world of knowledge, literature, and human experience.
Today, as we continue to discover new texts and artifacts, we’re reminded that the past still has secrets to reveal. The Rosetta Stone’s legacy lives on in every hieroglyph we read, every ancient story we uncover, and every connection we make with the people who lived along the Nile thousands of years ago. Did you ever imagine that a simple stone could hold such power over human understanding?




