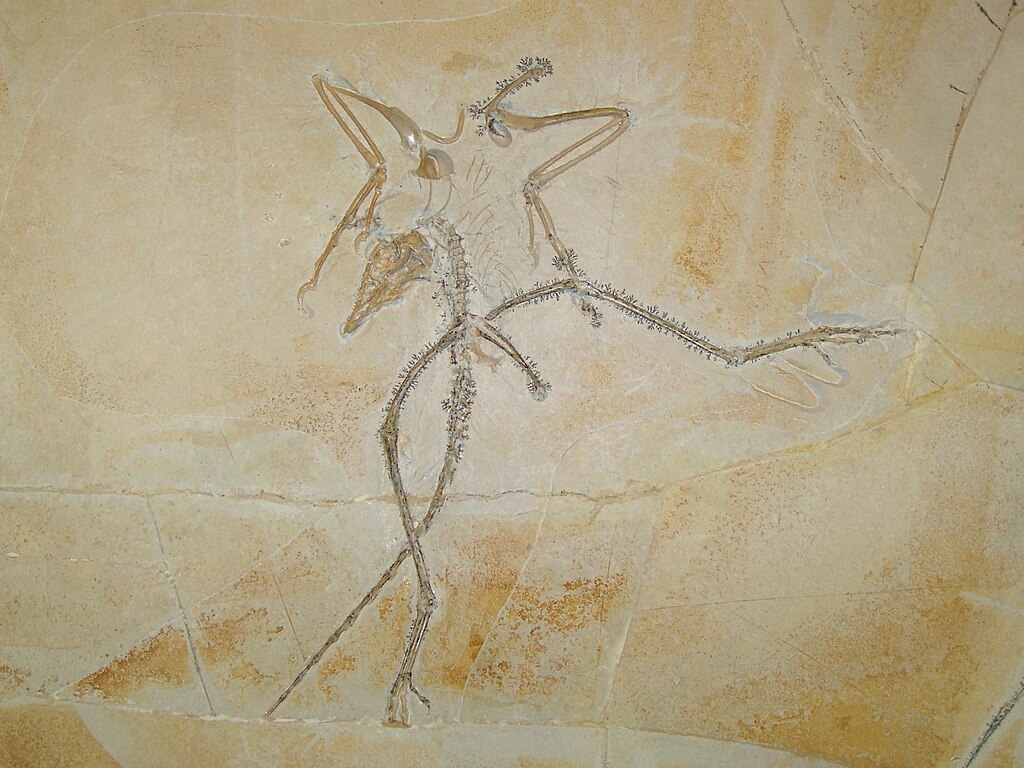
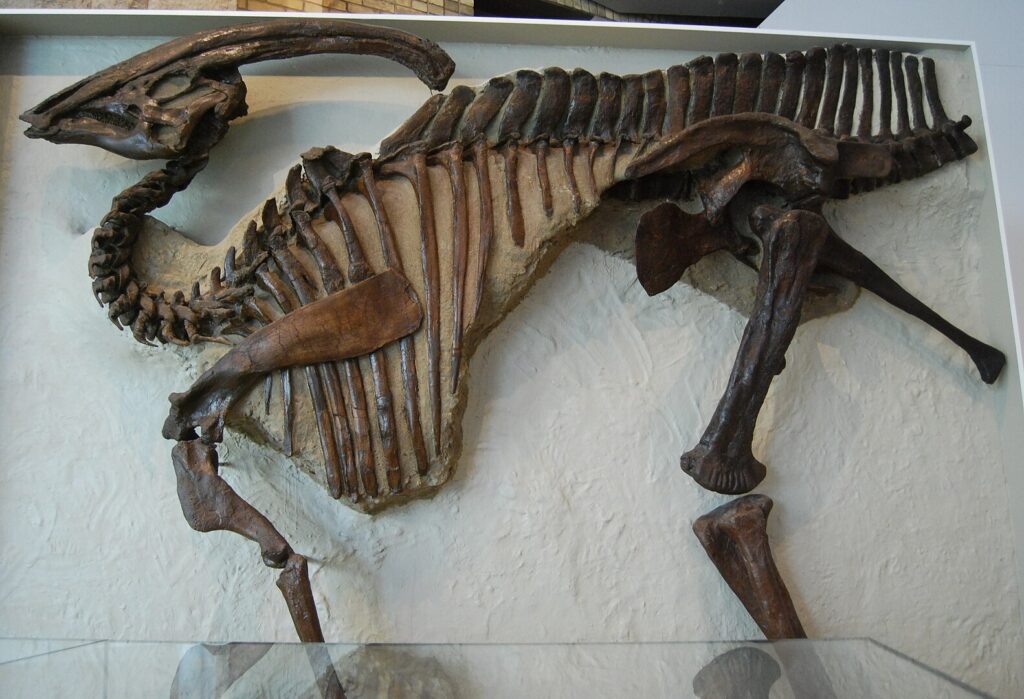
In the vast annals of paleontology, most discoveries fit neatly into taxonomic categories – a dinosaur limb here, a mammalian skull there. But occasionally, researchers unearth specimens that defy easy classification, leaving even seasoned experts scratching their heads in bewilderment. These mystery fossils represent some of the most intriguing challenges in paleontology, offering tantalizing glimpses into potentially unknown branches of the tree of life. Among these enigmatic finds, one particular specimen has generated significant scientific debate, earning the nickname “the fossil no one can identify.” This perplexing bone fragment has stumped experts across multiple disciplines, challenging our understanding of evolutionary history and highlighting the gaps that still exist in our knowledge of ancient life.
The Mysterious Discovery
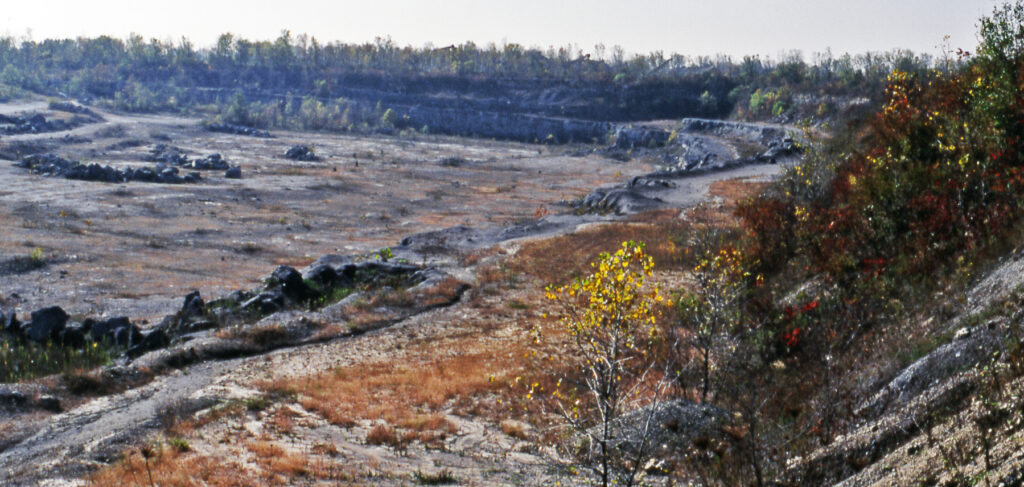

The unidentified fossil first emerged during a routine excavation in a remote limestone quarry in southern France in 2014. Unlike carefully planned paleontological digs, this discovery occurred accidentally when industrial mining operations exposed a previously untouched sedimentary layer estimated to be approximately 145 million years old, placing it at the boundary between the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous periods. The fossil itself appears to be a single bone fragment measuring approximately 32 centimeters in length, with several unusual morphological features that have confounded attempts at classification. Initially dismissed as a broken piece of pterosaur wing bone, closer examination revealed microstructures and developmental patterns inconsistent with known flying reptiles. The specimen’s unique combination of features has since sparked debate among paleontologists worldwide, with some suggesting it represents an entirely unknown taxonomic group.
Physical Characteristics That Puzzle Experts
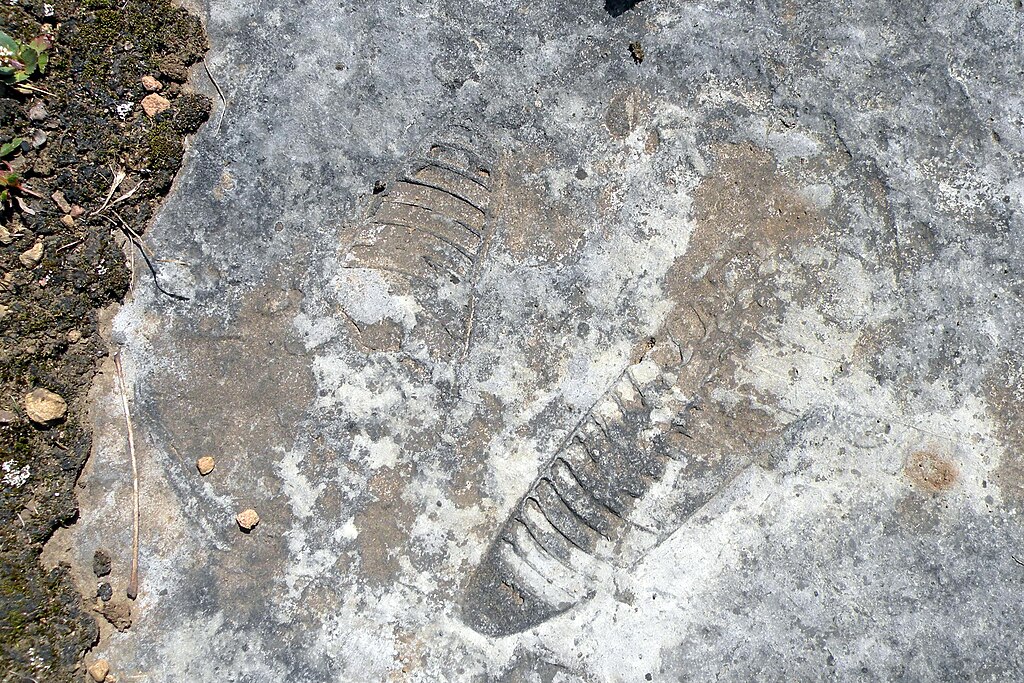

What makes this particular fossil so perplexing are its contradictory physical characteristics that seem to cross known taxonomic boundaries. The bone exhibits a distinctive honeycomb-like internal structure typically associated with avian species, suggesting lightweight construction optimized for flight or mobility. However, it also possesses dense cortical walls more typical of aquatic vertebrates adapted for ballast and buoyancy control. Adding to the mystery, the fossil displays attachment points for muscles in configurations not seen in any known extinct or extant species. Microscopic analysis has revealed growth patterns that combine aspects of both reptilian and early mammalian development, creating a morphological puzzle that defies current evolutionary models. Perhaps most baffling is the presence of small, channel-like structures throughout the bone, which some researchers believe may have housed a vascular system unlike any documented in the fossil record.
Dating Controversies
Establishing the precise age of the mystery fossil has proven nearly as challenging as identifying its taxonomic origins. Initial radiometric dating of the surrounding matrix suggested the specimen was approximately 145 million years old, placing it at the Jurassic-Cretaceous boundary. However, subsequent analysis using more sophisticated techniques yielded contradictory results, with some tests indicating the fossil might be significantly younger—perhaps 100 million years old—while others suggested it could be even older than initially thought. These inconsistencies have led some skeptics to question the fossil’s authenticity altogether. In contrast, others propose that the specimen might have been reworked from older sediments into younger layers through geological processes. The dating controversy adds another layer of complexity to an already perplexing scientific puzzle, as accurately placing the specimen in chronological context is crucial for understanding its evolutionary significance.
Competing Theories: Mammal, Reptile, or Bird?
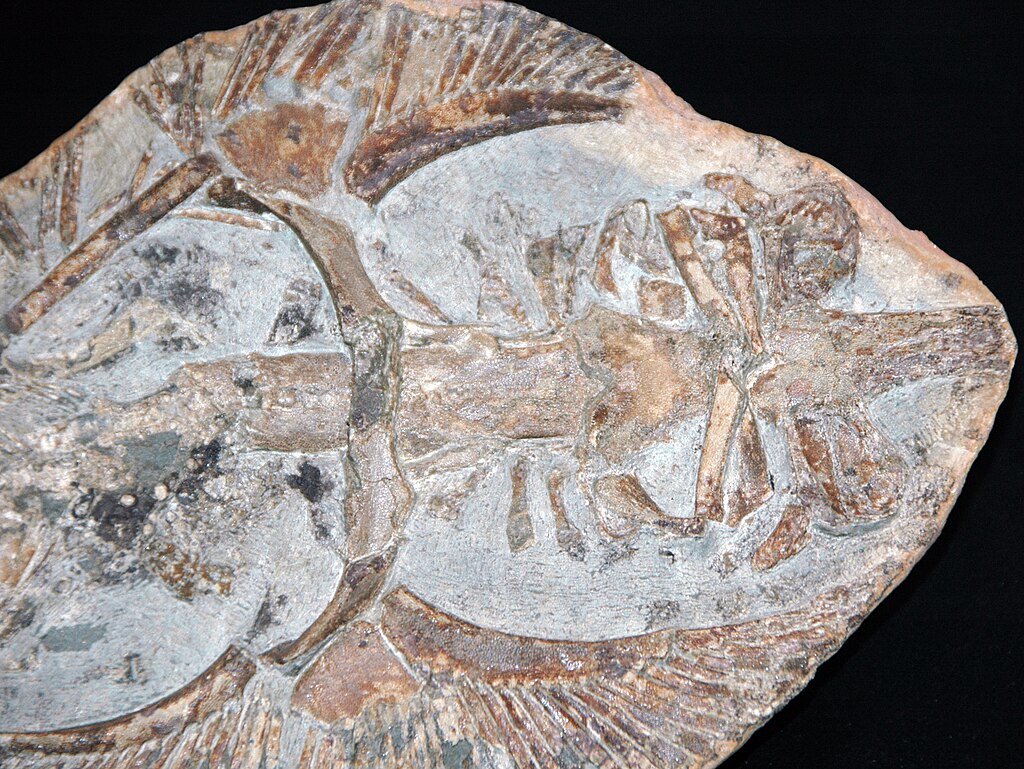

The scientific community remains divided on the taxonomic classification of the mystery fossil, with researchers falling into several competing camps based on their interpretation of the available evidence. One faction, led by prominent vertebrate paleontologist Dr. Eleanor Richter, argues that the specimen represents an early mammalian offshoot with unusual adaptations, pointing to specific microtextures in the bone consistent with mammalian growth patterns. A second group, headed by herpetological expert Professor Marcus Chen, presents compelling evidence that the fossil belongs to an unknown branch of marine reptiles, citing the density patterns and potential aquatic adaptations. Yet a third theory, championed by avian paleontologist Dr. Sofia Ahmadi, suggests the bone may come from a previously undocumented early bird or bird-like theropod dinosaur, referencing the pneumatic features and lightweight construction. Each theory addresses some aspects of the fossil’s unusual characteristics but fails to account for others, creating an ongoing scientific stalemate.
The “Hybrid Theory” Controversy

Perhaps the most controversial explanation for the unidentifiable fossil comes from a small but vocal group of researchers who have proposed what they call the “hybrid theory.” Proponents of this idea suggest that the specimen might represent an evolutionary chimera—a rare instance where two distinct evolutionary lineages converged or hybridized, creating organisms with mixed characteristics. Led by evolutionary biologist Dr. Jonathan Wei, these scientists point to the fossils’ contradictory features as evidence of genetic exchange between taxonomic groups previously thought incapable of interbreeding. This theory has been met with significant skepticism from the broader scientific community, with many respected paleontologists arguing that such hybridization would be biologically impossible between the distinct groups in question. Critics also note that verified cases of hybridization in the fossil record are exceedingly rare and typically occur between closely related species, not across major taxonomic boundaries as the hybrid theory would require.
Technological Approaches to Identification
As traditional morphological analysis has failed to resolve the mystery, researchers have turned to cutting-edge technologies in hopes of unlocking the fossil’s secrets. Advanced CT scanning has allowed scientists to create detailed three-dimensional models of the internal structure without damaging the precious specimen, revealing previously hidden features that may eventually prove crucial to identification. Synchrotron radiation analysis has provided insights into the chemical composition of the fossilized bone, showing unusual mineral concentrations that might reflect the organism’s environment or physiology. DNA extraction attempts have been made, though expectations remain low given the specimen’s age and the challenges of recovering genetic material from fossils millions of years old. Perhaps most promising is the application of machine learning algorithms that compare thousands of morphological features against databases of known species, searching for patterns that human researchers might miss. These technological approaches represent the frontier of paleontological research, offering new avenues for solving the mystery when traditional methods have reached their limits.
Geographic and Ecological Context

Understanding the environment where the mysterious fossil was deposited has become a crucial line of investigation for researchers seeking to identify the specimen. Paleoenvironmental reconstruction of the French quarry site indicates it was once part of a coastal ecosystem at the edge of the ancient Tethys Sea, characterized by shallow lagoons, tidal flats, and small islands. This transitional zone between marine and terrestrial habitats would have supported a diverse array of organisms adapted to multiple ecological niches. Microfossil analysis of the surrounding matrix has revealed an ecosystem rich in marine invertebrates, small fish, and various reptilian species, suggesting a productive environment with complex food webs. The presence of charcoal particles in the same sedimentary layer indicates periodic wildfire events on nearby land masses, potentially affecting population dynamics and fossilization patterns. This ecological context provides important clues about the lifestyle and adaptations of the mystery organism, narrowing the field of possibilities even as the exact identity remains elusive.
Similar Unidentified Fossils Throughout History
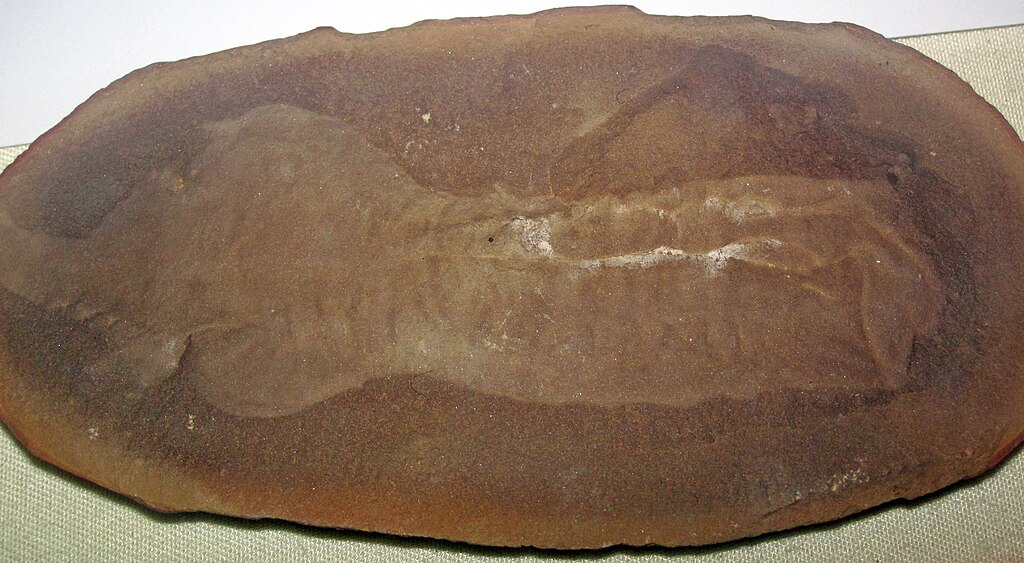

The current mystery fossil is far from the first specimen to confound the scientific community, joining a distinguished lineage of puzzling discoveries that have challenged taxonomic boundaries. Perhaps most famous among these historical enigmas was the “Tully Monster” (Tullimonstrum gregarium), discovered in Illinois in the 1950s and only tentatively classified as a vertebrate after more than six decades of scientific debate. Similarly, the Burgess Shale fossil Hallucigenia initially baffled paleontologists when discovered in the early 20th century, with researchers unsure which end was the head or even which side was up until relatively recent clarifications. The Ediacaran biota presents an entire assemblage of organisms so unlike later life forms that some scientists have proposed they represent a completely separate evolutionary experiment. These historical cases offer both perspective and caution for those studying the current mystery fossil, demonstrating that some taxonomic puzzles can take generations to solve while others may remain permanently ambiguous due to missing evidence or evolutionary patterns that don’t fit neatly into our current understanding of life’s history.
Authentication Challenges and Skepticism

Not all scientists are convinced that the mystery fossil represents a genuine biological puzzle, with a minority expressing skepticism about its authenticity or scientific significance. Some critics have suggested the unusual characteristics might result from taphonomic processes—post-mortem distortions that occurred during fossilization, rather than representing the original biological structure. Others point to the possibility of a composite specimen, either created naturally when multiple fossils were compressed together or, more controversially, fabricated to enhance commercial value. The fossil’s chain of custody has also come under scrutiny, as it passed through several private collections before reaching academic researchers, creating opportunities for potential manipulation or contamination. To address these concerns, the current research team has implemented rigorous authentication protocols, including multiple independent laboratory analyses and thorough documentation of the specimen’s physical and chemical properties. Despite these efforts, the shadow of skepticism continues to influence the scientific conversation, highlighting the importance of methodological rigor when dealing with potentially paradigm-shifting discoveries.
Implications for Evolutionary Theory

If ultimately authenticated and classified, the mystery fossil could have profound implications for our understanding of evolutionary history. The specimen’s unusual combination of features challenges conventional models of trait development and inheritance, potentially indicating evolutionary pathways not reflected in current taxonomic frameworks. Some researchers suggest the fossil might represent an example of convergent evolution—where similar traits evolve independently in unrelated lineages—taken to an extreme degree not previously documented. Others propose it could evidence a “ghost lineage,” a hypothetical evolutionary branch that existed but left few traces in the fossil record due to factors like small population size or environments unfavorable to preservation. The most dramatic interpretation suggests the specimen might force a reconsideration of traditional evolutionary trees, particularly around the diversification of tetrapods during the Mesozoic Era. Regardless of its final classification, the mystery fossil highlights the dynamic nature of evolutionary science and the continuing capacity for discoveries to reshape established theories about life’s history on Earth.
The International Research Consortium
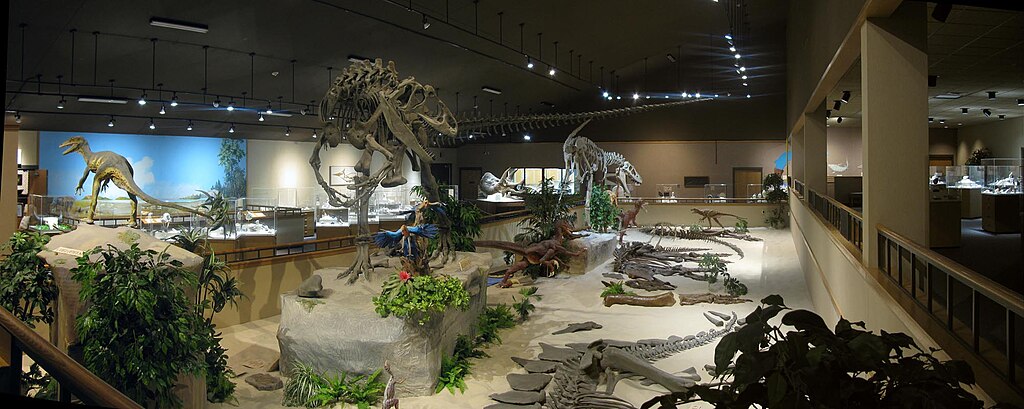

Recognizing the exceptional scientific importance of the unidentified fossil, an international research consortium was established in 2018 to coordinate investigation efforts across disciplinary and institutional boundaries. The consortium brings together specialists from twenty-three universities spanning twelve countries, including experts in vertebrate paleontology, evolutionary developmental biology, geochemistry, and advanced imaging technologies. This collaborative approach has allowed for unprecedented resource sharing and methodological cross-pollination, with research protocols designed to maximize data collection while minimizing damage to the irreplaceable specimen. The consortium operates under a transparent open-science framework, with all findings immediately shared among member institutions and regularly published in peer-reviewed journals regardless of whether they support or contradict previous hypotheses. Regular symposia allow researchers to debate interpretations face-to-face, while standardized analytical techniques ensure results can be meaningfully compared across different laboratories. This model of scientific cooperation represents a gold standard for investigating challenging paleontological specimens, maximizing the collective intelligence of the scientific community rather than relying on isolated experts working in institutional silos.
Public Fascination and Media Coverage

Beyond its scientific significance, the mystery fossil has captured public imagination through extensive media coverage that highlights the allure of unsolved scientific puzzles. Major documentaries produced by National Geographic and the BBC have brought the mysterious specimen into living rooms worldwide, using sophisticated animations to visualize competing theories about the organism’s appearance and lifestyle when alive. Social media discussions about the fossil regularly trend among science enthusiasts, with hashtags like #MysteryBone and #FossilDetective generating millions of engagements. This public interest has proven double-edged for researchers, generating valuable awareness and funding opportunities while sometimes leading to sensationalized reporting that overstates certain theories or prematurely declares breakthroughs. Museums featuring casts of the specimens report significant attendance increases, demonstrating the powerful draw of scientific mysteries compared to fully explained exhibits. Some paleontologists have embraced this public fascination as an educational opportunity, using the unidentified fossil as a teaching tool to explain how science handles uncertainty and how knowledge advances through the testing and refinement of multiple competing hypotheses.
The Future of the Investigation

As research into the mystery fossil continues, several promising avenues may eventually lead to its identification. The consortium has prioritized recovering additional specimens from the original quarry site, with focused excavations planned for the next five field seasons to search for complementary fossils that might complete the partial specimen or provide contextual information. Advances in microscopy and chemical analysis techniques continue to reveal new details about the bone’s composition and structure, with researchers particularly hopeful about emerging technologies for ancient protein sequencing that might provide phylogenetic data even when DNA is unrecoverable. Comparative databases of known fossil morphologies grow more comprehensive each year, increasing the likelihood of finding meaningful anatomical parallels. Perhaps most intriguingly, several researchers have proposed that the mystery may ultimately be solved not through the specimen itself but by discoveries of similar organisms elsewhere, filling gaps in our understanding of Mesozoic biodiversity. While some scientists believe the fossil may remain permanently unclassifiable due to its unique characteristics, most remain optimistic that persistent investigation combined with technological advancement will eventually reveal the true identity of this paleontological puzzle.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the unidentified fossil represents more than just a scientific curiosity—it embodies the very essence of paleontological research, where fragments of ancient life challenge us to expand our understanding of evolutionary history. Whether eventually classified within known taxonomic categories or recognized as something entirely new, the specimen has already made a significant contribution to science by stimulating innovative research methodologies and international collaboration. As the investigation continues, it reminds us that despite centuries of scientific progress, the natural world still holds mysteries capable of confounding our most sophisticated analytical techniques and challenging our conceptual frameworks. In this sense, the fossil no one can identify serves as both a humbling reminder of the limits of current knowledge and an inspiring catalyst for the next generation of scientific discovery.




